Apple's latest M3 Pro chip in the new 14-inch and 16-inch MacBook Pro has 25% less memory bandwidth than the M1 Pro and M2 Pro chips used in equivalent models from the two previous generations.

Based on the latest 3-nanometer technology and featuring all-new GPU architecture, the M3 series of chips is said to represent the fastest and most power-efficient evolution of Apple silicon thus far. For example, the 14-inch and 16-inch MacBook Pro with M3 Pro chip is up to 40% faster than the 16-inch model with M1 Pro, according to Apple.
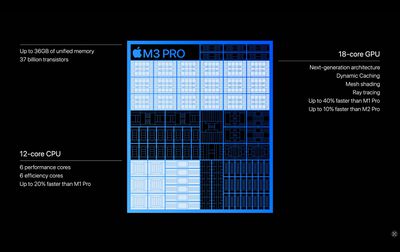
However, looking at Apple's own hardware specifications, the M3 Pro system on a chip (SoC) features 150GB/s memory bandwidth, compared to 200GB/s on the earlier M1 Pro and M2 Pro. As for the M3 Max, Apple says it is capable of "up to 400GB/s." This wording is because the less pricey scaled-down M3 Max with 14-core CPU and 30-core GPU has only 300GB/s of memory bandwidth, whereas the equivalent scaled-down M2 Max with 12-core CPU and 30-core GPU featured 400GB/s bandwidth, just like its more powerful 12‑core CPU, 38‑core GPU version.
Notably, Apple has also changed the core ratios of the higher-tier M3 Pro chip compared to its direct predecessor. The M3 Pro with 12-core CPU has 6 performance cores (versus 8 performance cores on the 12-core M2 Pro) and 6 efficiency cores (versus 4 efficiency cores on the 12-core M2 Pro), while the GPU has 18 cores (versus 19 on the equivalent M2 Pro chip).
Additionally, while the M3 chip's 16-core Neural Engine has the same number of cores as the one Apple featured in the 3nm-based A17 Pro chip that debuted in the iPhone 15 Pro series in September, it's comparatively weaker on paper in terms of maximum achievable throughput, which is measured in trillions of operations per second (TOPS).
According to Apple, the M3 Neural Engine is capable of 18 TOPS, whereas the A17 Pro Neural Engine is capable of 35 TOPS. It's hard to say for certain, but it is possible that the iPhone 15 Pro requires a higher performing Neural Engine for features like computational photography and Face ID, whereas the M3 can compensate in other areas like machine learning by utilizing its additional GPU cores.
Taken together, it's presently unclear what real-world difference these changes make to M3 performance when pitted against Apple's equivalent precursor chips in various usage scenarios, especially given that the latest processors include new Dynamic Caching memory allocation technology which ensures that only the exact amount of memory needed is used for each task.
This opaqueness is not helped by the fact that Apple advertises the power of the new M3 Pro and M3 Max chips by repeatedly emphasizing comparisons to the M1 Pro and M1 Max, rather than the more recent M2 variants, against which performance gains appear more modest. Hopefully we will learn more in time when the first thoroughgoing third-party benchmarks become available.
The new MacBook Pro models are available to order now, and they will begin arriving to customers and launch in stores on Tuesday, November 7. Be sure to check out our MacBook Pro announcement coverage for all the details.