An estimated 1 in 3 Americans are exposed to harmful levels of noise on a regular basis, based on data gathered as part of the Apple Hearing Study. In recognition of International Noise Awareness Day, University of Michigan researchers working on the hearing study in partnership with Apple shared a blog post noise exposure.
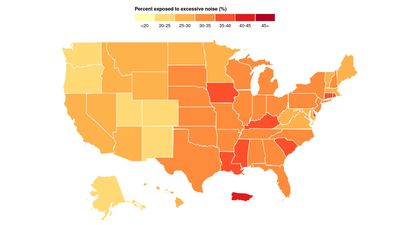
Extrapolating data collected from 130,000 Apple Hearing Study volunteers who contributed readings from their Apple Watch between November 2019 and December 2022, the University of Michigan estimated that 77 million adults across the United States are consistently exposed to high noise levels.
According to the World Health Organization and the United States Environmental Protection Agency, an annual average noise exposure level of 70 decibels (dBA) poses no risk for hearing loss, but exposure over 70 dBA can result in damage to hearing.
The study assumes that people with repeated daily average noise exposures over 70 dBA likely have an annual noise exposure over 70 dBA, which researchers say can result in hearing issues, irritation, heart problems, and sleep disturbances, in addition to impacting mental health. Higher noise levels for longer time periods can increase risk.

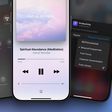
The Apple Watch has a built-in feature for detecting environmental sound level, and it collects data to tabulate an average daily environmental sound exposure level. The information collected by the watch can be located in the Hearing section of the Health app.
The Health app will let you know if your noise exposure levels are below 75 dB on average and are "OK," or if you have been repeatedly exposed to higher levels of sound that can impact your health. At 80 dB, 40 hours of exposure over seven days could potentially result in damage, but at 120 dB, 14 seconds over seven days could cause problems. The Apple Watch is able to send an alert when it detects a harmful noise level so you can move to a quieter location.
People in Puerto Rico, Delaware, Rhode Island, Mississippi, and Connecticut experienced the highest noise pollution levels, and adults aged 35 to 44 were more likely to be exposed to high noise levels compared to those in other age groups.
Additional details about the study can be found in the full blog post on the University of Michigan website. To cut down on hearing damage, researchers recommend that those regularly exposed to excessive noise pollution move away from noisy areas and take "quiet breaks," buy quiet appliances, and wear ear muffs and ear plugs when possible.