Consumer spending on the top 100 non-game subscription-based apps across mobile platforms grew 41% year-on-year to $18.3 billion in 2021, up from 13 billion in 2020, according to a new report from analytics firm Sensor Tower.
According to the data, revenue from subscription apps purchased on the App Store and the Google Play Store represented around 14% of the $131.6 billion that consumers spent on in-app purchases last year, up from 11.7% in 2020.
In the fourth quarter of 2021, however, 86 of the top 100 earning non-game apps worldwide offered subscriptions, which is actually down slightly from 87 in the same quarter of 2020.
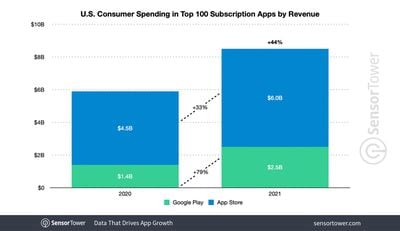
In keeping with historical trends, spending on subscription-based apps in Apple's App Store was vastly more than in the Google Play Store:
As in previous years, consumers spent more on subscription-based apps downloads from the App Store than on Google Play. The top 100 non-game subscription apps on the App Store generated $13.5 billion in 2021, up 31 percent Y/Y from $10.3 billion. Worldwide consumers spent $4.8 billion on the top 100 subscription apps on Google's marketplace, up 78 percent from $2.7 billion in 2020. While the top subscription apps on Google Play experienced more growth, the top apps on the App Store saw nearly three times as much spending last year.
Like in 2020, the only performance indicator in which the Google Play Store beat the App Store was in terms of year-on-year growth for U.S. user spending on subscription apps.
Consumer spending in the U.S. saw a similar breakdown, with the top 100 subscription apps generating $6 billion on the App Store, up 33 percent Y/Y from $4.5 billion. The cohort saw approximately $2.5 billion in consumer spending on Google Play, up 79 percent from $1.4 billion in 2020.
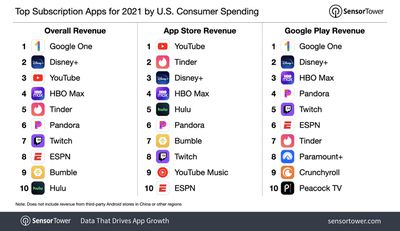
Google parent company Alphabet was once again the big winner this year in terms of subscription app spending, both globally and in the U.S. YouTube generated $1.2 billion worldwide and $566.5 million in the U.S., while Google One saw $1.1 billion worldwide and $698 million in the U.S. in 2021.
Despite the numbers, subscription-based apps generally divide App Store users between those for and against the revenue model. Apple began incentivizing developers to sell their apps for a recurring fee instead of a one-time cost when it made changes to its App Store subscription policies in 2016. Usually, Apple takes 30 percent of app revenue, but developers who are able to maintain a subscription with a customer longer than a year see Apple's cut drop down to 15 percent.
In late 2017, Apple began letting developers offer discounted introductory pricing and time-limited free trials on auto-renewable app subscriptions, based on the idea that subscriptions provide a higher likelihood of an engaged audience.























