Apple made unusual mid-production hardware changes to the A12, A13, and S5 processors in its devices in the fall of 2020 to update the Secure Storage Component, according to Apple Support documents.

According to an Apple Support page, spotted by Twitter user Andrew Pantyukhin, Apple changed the Secure Enclave in a number of products in the fall of 2020:
Note: A12, A13, S4, and S5 products first released in Fall 2020 have a 2nd-generation Secure Storage Component; while earlier products based on these SoCs have 1st-generation Secure Storage Component.
The Secure Enclave is a coprocessor that is used for data protection and authentication with Touch ID and Face ID. The purpose of the Secure Enclave is to handle keys and other information, such as biometrics, that are sensitive enough to not be handled by the Application Processor. This data is stored in a Secure Storage Component inside the Secure Enclave, which is the specific part that Apple changed last year.
The explanation in Apple's support document suggests, at minimum, that the eighth-generation entry-level iPad, Apple Watch SE, and HomePod mini have different Secure Enclaves compared to older devices with the same chip.
However, there are a number of discrepancies in Apple's support document. Despite Apple explaining that A13 products "first released in Fall 2020 have a 2nd-generation Secure Storage Component," there was no device with an A13 chip "first released in Fall 2020." The last device to be released with an A13 chip was the iPhone SE in February 2020.
If the change was, in fact, made to all newly-manufactured devices with these chips, the affected devices would include the iPhone XR, iPhone 11, iPhone SE, and fifth-generation iPad mini, as well as the newly-released eighth-generation iPad, Apple Watch SE, and HomePod mini.
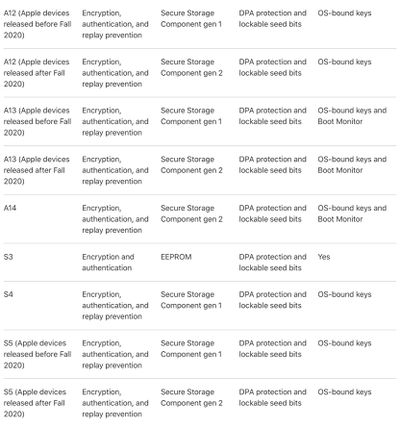
To make matters more confusing, the table listing the multiple versions of the Secure Enclave's storage component in the feature summary omits the S4 chip with a second-generation Secure Storage Component, despite the rubric claiming that such a chip exists. The Apple Watch Series 4 was the only device to contain an S4 chip, and this device was discontinued in September 2019, long before the second-generation Secure Storage Component was implemented in the fall of 2020. It is possible that part of this lack of clarity relates to the fact that the A12 and S4 chips introduced the first-generation Secure Storage Component.
New devices containing the A14 or S6 chip, such as the iPhone 12, iPhone 12 Pro, fourth-generation iPad Air, and Apple Watch Series 6, also have the updated Secure Enclave.
Although the change took place in the fall of 2020, the support document detailing the alteration was published in February 2021. The full PDF version of Apple's Platform Security Guide reveals the difference between the first and second-generation Secure Storage Component:
The 2nd-generation Secure Storage Component adds counter lockboxes. Each counter lockbox stores a 128-bit salt, a 128-bit passcode verifier, an 8-bit counter, and an 8-bit maximum attempt value. Access to the counter lockboxes is through an encrypted and authenticated protocol.
Counter lockboxes hold the entropy needed to unlock passcode-protected user data. To access the user data, the paired Secure Enclave must derive the correct passcode entropy value from the user's passcode and the Secure Enclave's UID. The user's passcode can't be learned using unlock attempts sent from a source other than the paired Secure Enclave. If the passcode attempt limit is exceeded (for example, 10 attempts on iPhone), the passcode-protected data is erased completely by the Secure Storage Component.
This appears to be a countermeasure against password-cracking devices, such as GrayKey, which attempt to break into iPhones by guessing the passcode an infinite number of times, using exploits that allow for infinite incorrect password attempts.
The change appears to have been significant enough for Apple to justify an entire "second-generation" version of the Secure Enclave's storage. It is certainly unusual for Apple to change a component in its chips mid-way through production, but Apple likely deemed the security upgrade important enough to roll it out to all relevant new devices from the fall onwards, rather than just devices with the latest A14 and S6 chips.