Apple is researching how it can reduce the appearance of fingerprints and smudges on the metal surfaces of its products and has hinted yet again at the use of titanium for future Apple devices, according to newly-granted patent filings.
 Image via Dbrand
Image via DbrandThe patent, filed with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and spotted by Patently Apple, is titled "Oxide coatings for metal surfaces" and explains in detail how a thin coating can significantly reduce the appearance of fingerprints on devices.
Last month, patents for titanium device enclosures came to light, revealing Apple's interest in how various devices, including MacBooks, iPads, and iPhones, could adopt titanium casings with a distinctive textured finish. Now, Apple's patent for oxide coatings has again stressed the advantages of using titanium on consumer electronics, such as "high strength, stiffness, and hardness."
For example, the relatively high hardness of titanium makes it resistant to scratches, and its stiffness makes it durable enough to withstand bending. In addition, titanium is inherently more corrosion-resistant than certain other alloys.
Apple highlights that, compared to other metals, titanium easily shows fingerprints when handled. This is partially due to the relatively low reflectivity of titanium and titanium alloy surfaces.
One of the disadvantages of using titanium and its alloys, however, is that oil from fingerprints can be readily seen on bare titanium and titanium alloy surfaces, leaving unattractive marks on consumer electronics. The nature and volume of the fingerprints can be factors, but even clean fingers can leave a relatively dramatic mark on titanium surfaces.

Conventional oleophobic coatings are usually used to reduce fingerprinting on glass surfaces such as the front and back of iPhones, but these types of coatings are much less effective on titanium surfaces. The patent suggests that Apple's interest in using titanium for its devices has led to the need for new, more effective solutions for the prevention of fingerprinting.
What are needed therefore are improved cosmetic surface finishes for titanium and its alloys.
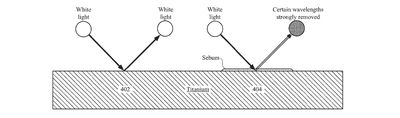
This has led the company to research the use of a thin oxide coating or film "configured to reduce or eliminate interference-coloring effects brought upon by fingerprints or other thin film options." Apple's oxide coating allows the surface of a device to continue reflecting light as though there is no fingerprint present, thereby hiding oily smudges.
In some embodiments, the oxide coatings are sufficiently thick to increase the optical path difference of incident light, thereby reducing any inference coloring by the fingerprint to a non-visible level. In some embodiments, the oxide coatings have a non-uniform thickness that changes the way light reflects off interfaces of the oxide coating, thereby reducing or eliminating any thin film interference coloring.
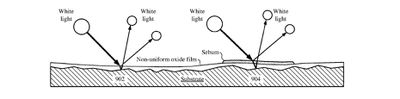
Apple also notes that an oxide coating could be used on surfaces including "aluminum, aluminum alloy, steel, magnesium, magnesium alloys, zirconium, or zirconium alloys," even though it was developed primarily to address titanium or titanium alloys.
The filing also highlights that the oxide coating can be used "to form durable and cosmetically appealing finishes" on a wide range of Apple devices, including the iPad, iPhone, Apple Watch, and MacBook.
Following last month's news of Apple's curiosity about expanding the use of titanium for its devices, which is currently only available on the Apple Watch Edition, it is interesting that research in the area is leading to other technological innovations.
Apple's research suggests that the company is looking to move beyond standard anodized aluminum casings, but there is no telling if and when this may happen. Nonetheless, patent filings can provide insight into what Apple is exploring and developing behind the scenes, and hint at what we could see in the future.























