The second known piece of malware that has been compiled to run natively on M1 Macs has been discovered by security firm Red Canary.

Given the name "Silver Sparrow," the malicious package is said to leverage the macOS Installer JavaScript API to execute suspicious commands. After observing the malware for over a week, however, neither Red Canary nor its research partners observed a final payload, so the exact threat that the malware poses remains a mystery.
Nevertheless, Red Canary said the malware could be "a reasonably serious threat":
Though we haven't observed Silver Sparrow delivering additional malicious payloads yet, its forward-looking M1 chip compatibility, global reach, relatively high infection rate, and operational maturity suggest Silver Sparrow is a reasonably serious threat, uniquely positioned to deliver a potentially impactful payload at a moment's notice.
According to data provided by Malwarebytes, "Silver Sparrow" had infected 29,139 macOS systems across 153 countries as of February 17, including "high volumes of detection in the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, France, and Germany." Red Canary did not specify how many of these systems were M1 Macs, if any.
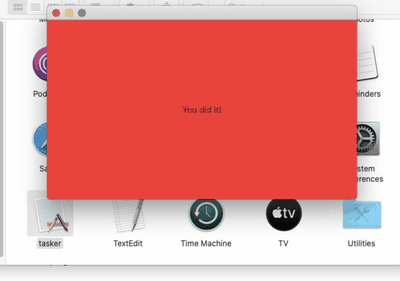
Given that the "Silver Sparrow" binaries "don't seem to do all that much" yet, Red Canary referred to them as "bystander binaries." When executed on Intel-based Macs, the malicious package simply shows a blank window with a "Hello, World!" message, while the Apple silicon binary leads to a red window that says "You did it!"
Red Canary shared methods for detecting a wide array of macOS threats, but the steps are not specific to detecting "Silver Sparrow":
- Look for a process that appears to be PlistBuddy executing in conjunction with a command line containing the following: LaunchAgents and RunAtLoad and true. This analytic helps us find multiple macOS malware families establishing LaunchAgent persistence.
- Look for a process that appears to be sqlite3 executing in conjunction with a
command line that contains: LSQuarantine. This analytic helps us find multiple macOS malware families manipulating or searching metadata for downloaded files.
- Look for a process that appears to be curl executing in conjunction with a command line that contains: s3.amazonaws.com. This analytic helps us find multiple macOS malware families using S3 buckets for distribution.
The first piece of malware capable of running natively on M1 Macs was discovered just days ago. Technical details about this second piece of malware can be found in Red Canary's blog post, and Ars Technica has a good explainer as well.