Intel today announced the launch of its latest 10th-generation Core processors for high-end notebooks, potentially including the next 16-inch MacBook Pro. The batch of 45W chips, part of the Comet Lake family, are built on Intel's 14nm++ architecture.

The new H-series chips have the same base clock speeds as the 9th-generation chips in the current 16-inch MacBook Pro, but Turbo Boost speeds now exceed 5GHz for the first time. For example, the new highest-end Core i9 chip still clocks in at 2.4GHz, but its maximum Turbo Boost frequency has increased from 5.0GHz to 5.3GHz.
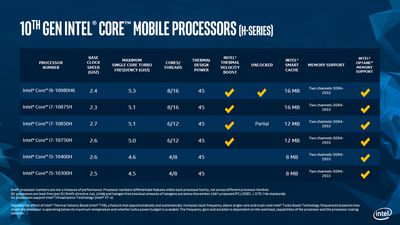
Intel promotes the fact that its new Core i9 chip is the "world's fastest mobile processor" and the first to exceed the 5GHz frequency barrier. However, not everyone is impressed with the year-over-year performance improvements as a whole.
I think it’s fair to scoff at re-releasing the same CPU as last year’s with only minor changes to clock speed. — Paul Haddad (@tapbot_paul) April 2, 2020
The new 10th-generation processors also support Wi-Fi 6, aka 802.11ax. The newer standard delivers faster speeds, greater network capacity, improved power efficiency, lower latency, and connectivity improvements in areas with several Wi-Fi devices. Wi-Fi 6 devices must support WPA3, a Wi-Fi security protocol with improved cryptographic strength.
Apple added Wi-Fi 6 to its latest iPhone and iPad Pro models, but the 16-inch MacBook Pro and the new MacBook Air still have Wi-Fi 5.
The existing 16-inch MacBook Pro launched in November 2019, so it is still relatively early for the notebook to receive an update. In the near term, it is more likely that the 13-inch MacBook Pro will be updated with a Magic Keyboard and faster processors, with the next 16-inch MacBook Pro refresh likely to come later in the year.
Keep in mind that last month, analyst Ming-Chi Kuo said Apple's first Mac notebooks with its own custom-designed Arm-based processors will launch in the fourth quarter of 2020 or the first quarter of 2021. Kuo said Apple plans to launch several Arm-based Macs by the end of 2021, including notebooks and desktops, marking a transition away from Intel.























