At its WWDC keynote on Monday, Apple unveiled its new login feature that will allow users to sign into apps and websites using their Apple ID. As part of iOS 13, Apple will require all apps that use third-party sign-in options to include its Sign In With Apple button.
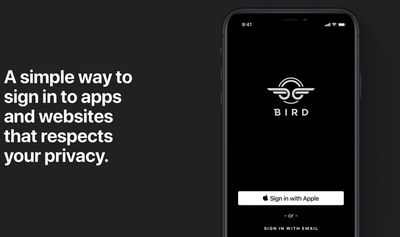
The feature has been largely welcomed as a more secure alternative to similar sign-in services offered by Facebook, Google, and Twitter, since it authenticates the user with Face ID or Touch ID, and doesn't send personal information to app and website developers.
However, one detail in Apple's updated Human Interface Guidelines is raising eyebrows – Apple is asking developers to position its Sign In with Apple button more prominently by putting it above all other rival sign-in options.
The guidelines are regarded as suggestions about how developers should build their apps, rather than mandatory requirements. Even so, many developers believe that following the guidelines gives their apps the best chance of passing Apple's approval process. Curiously, Apple is also asking developers to place its Sign In with Apple button above other options on websites, an area over which it wields no review power.
The suggestions come at a time when developers and rivals have claimed some of Apple's business practices, such as taking up to a 30 percent commission on apps sold through its App Store, are unfair and anticompetitive, and amount to operating the platform as a monopoly.
In the EU, antitrust regulators are looking into claims by Spotify that it is using the App Store to deliberately disadvantage other app developers. Meanwhile in the U.S., the Department of Justice was recently given the go ahead by the Federal Trade Commission to launch a probe into Apple's business practices, as part of a broader review of antitrust concerns in relation to large technology companies.
In an interview yesterday with CBSNews, Apple CEO Tim Cook said that scrutiny of Apple's business practices was "fair" and a good thing for large companies, but claimed the company is not a monopoly in any of the markets it operates in.