The New York Times today published a story explaining why Apple is unlikely to manufacture more of its products in the United States.
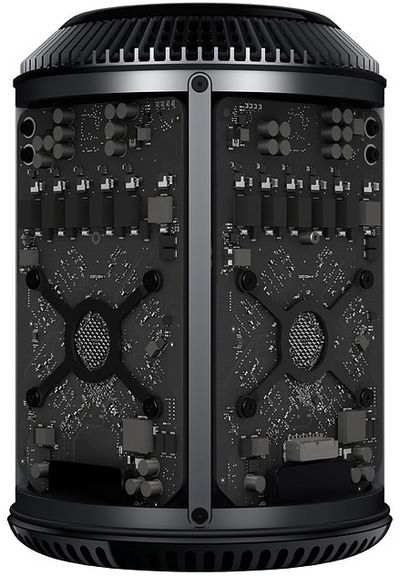

The report reveals an interesting anecdote about the latest Mac Pro. In late 2012, Apple CEO Tim Cook touted that the computer would be "Made in the USA," but sales were supposedly postponed by months in part because Apple could not secure enough custom screws for the computer from U.S.-based suppliers.
A machine shop in Texas tasked with the job could produce at most 1,000 screws a day, according to the report. By the time the computer was ready for mass production, this shortage gave Apple little choice but to order screws from China where factories can produce vast quantities of custom screws on short notice.
Apple's manufacturing partner eventually turned to another Texas supplier in Caldwell Manufacturing, which was hired to make 28,000 screws, the report adds. That company delivered 28,000 screws over 22 trips, with its owner Stephen Melo often "making the one-hour drive himself in his Lexus sedan."
The report goes on to describe how the United States struggles to compete with China's combination of scale, skills, infrastructure, and cost. In short, American workers are typically more expensive and unwilling to work around the clock.
In response to the report, an Apple spokesperson told The New York Times that Apple was "an engine of economic growth in the United States" that spent $60 billion last year with 9,000 American suppliers, helping to support 450,000 jobs.
Apple has promised to release a new Mac Pro in 2019, but it's unclear where it will be manufactured.
Update: MacRumors has obtained Apple's full statement regarding this topic, consistent with a press release it has shared on Apple Newsroom:
Apple is proud to be an engine of economic growth in the United States, supporting two million jobs across all fifty states. Last year our spend with 9,000 American component suppliers and companies increased more than 10 percent to $60 billion, supporting over 450,000 jobs. Every one of our core products contains parts or materials from the US or is made with equipment from US suppliers, and we work with manufacturing locations in 38 states.
The revolutionary Face ID that unlocks iPhone and iPad Pro is powered in part by vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs) made by Finisar in Allen, Texas. iPhone and iPad include glass made by Corning in Harrodsburg, Kentucky. And Broadcom in Fort Collins, Colorado, Qorvo in Hillsboro, Oregon and Skyworks in Woburn, Massachusetts all make parts to enable seamless wireless connectivity around the world.
Last year we confirmed our direct contributions in the US would top $350 billion by 2023 and we are on track to meeting that commitment. From corporate employees and our retail teams, to app developers, manufacturing workers and logistics employees, Apple is creating jobs across the country and we are deeply committed to advancing American innovation.