Apple today announced that it will be rebuilding its Maps app "from the ground up" with street-level data collected from its fleet of Apple Maps vehicles, high resolution satellite imagery, and anonymized, random segments of navigation sessions from iPhone users, which Apple refers to as "probe data."
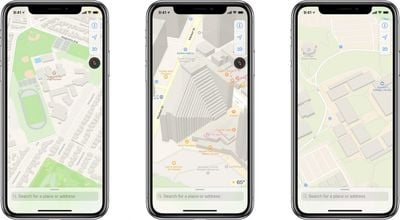
TechCrunch's Matthew Panzarino has published an in-depth overview of the changes coming to Apple Maps, which will be available in the San Francisco area starting with the next iOS 12 beta next week, cover all of Northern California by this fall, and roll out across the rest of the United States over the next year.
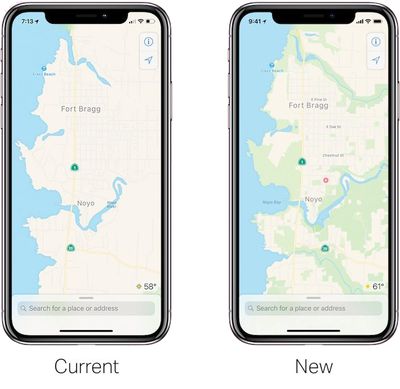
In short, Panzarino says Apple Maps will be switching to its own base map, reducing but not fully eliminating its reliance on third-party providers like TomTom, which will yield significant improvements to traffic, real-time road conditions, road systems, new construction, changes in pedestrian walkways, and more.
Apple also promises more relevant search results that, as Panzarino quips, are hopefully on the same continent now.
In a follow-up question-and-answer piece, Panzarino noted Apple Maps will more accurately display foliage like grass and trees, pools, parking lots, exact building shapes, sports areas like baseball diamonds, tennis and basketball courts, and pedestrian pathways that are commonly walked but previously unmapped.
His questionnaire also confirms that the overall design of Apple Maps will remain similar for now, beyond the additional detail.
Panzarino spoke in detail about the changes with Apple senior vice president Eddy Cue, who oversees Apple Maps:
"Since we introduced this six years ago — we won't rehash all the issues we've had when we introduced it — we've done a huge investment in getting the map up to par," said Cue. "When we launched, a lot of it was all about directions and getting to a certain place. Finding the place and getting directions to that place. We've done a huge investment of making millions of changes, adding millions of locations, updating the map and changing the map more frequently. All of those things over the past six years."
Cue noted further improvements will take Apple Maps to "the next level":
"We wanted to take this to the next level," says Cue. "We have been working on trying to create what we hope is going to be the best map app in the world, taking it to the next step. That is building all of our own map data from the ground up."
More from Cue:
"We don't think there's anybody doing this level of work that we're doing," adds Cue. "We haven't announced this. We haven't told anybody about this. It's one of those things that we've been able to keep pretty much a secret. Nobody really knows about it. We're excited to get it out there. Over the next year, we'll be rolling it out, section by section in the US."
Cue's notion that nobody really knew about these plans is debatable, as its Apple Maps vehicles have been a telltale sign since 2015, the same year Mark Gurman reported that Apple would switch to its own base map by 2018.
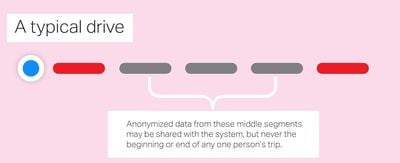
Apple's in-house base map will continue to improve thanks to probe data. When an iPhone user is navigating with Apple Maps, Apple may collect anonymized data from middle segments of the trip, but never the beginning or end point. Apple says no personal information is ever attached to the data it receives.
The secret sauce here is what Apple calls probe data. Essentially little slices of vector data that represent direction and speed transmitted back to Apple completely anonymized with no way to tie it to a specific user or even any given trip. It’s reaching in and sipping a tiny amount of data from millions of users instead, giving it a holistic, real-time picture without compromising user privacy.
Despite the privacy push, iPhone users can still disable the collection of probe data from their device, if they so desire, by opening the Settings app and tapping Privacy > Location Services > Maps > Never.
In addition to improved accuracy, Cue said Apple will be able to quickly make changes and updates to its base map, such as new roads:
"For example, a road network is something that takes a much longer time to change currently. In the new map infrastructure, we can change that relatively quickly. If a new road opens up, immediately we can see that and make that change very, very quickly around it. It's much, much more rapid to do changes in the new map environment."
Apple did not confirm when the improvements could reach other countries, but Cue noted that the Apple Maps team is global, and Apple Maps vehicles have already surveyed parts of at least ten other countries, including Croatia, France, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Portugal, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, and the United Kingdom.
Apple also hasn't confirmed if it will use the data it collects to eventually introduce its own street view feature like Google Maps.
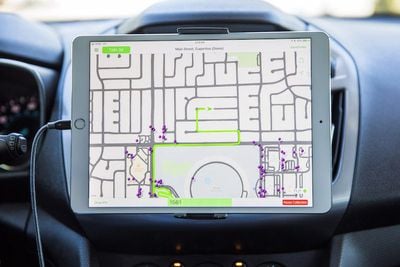
The full article is well worth a read, diving deep into advanced technologies like 3D point clouds and Deep Lambertian Networks that Apple is using to parse its mapping data. Panzarino was also invited for a ride in an Apple Maps vehicle, and he shared interesting photos and details about their setup.
TechCrunch: Apple is rebuilding Maps from the ground up