Hackers have had an "easy way" to get certain malware past signature checks in third-party security tools since Apple's OS X Leopard operating system in 2007, according to a detailed new report today by Ars Technica. Researchers discovered that hackers could essentially trick the security tools -- designed to sniff out suspiciously signed software -- into thinking the malware was officially signed by Apple while they in fact hid malicious software.
The researchers said that the signature bypassing method is so "easy" and "trivial" that pretty much any hacker who discovered it could pass off malicious code as an app that appeared to be signed by Apple. These digital signatures are core security functions that let users know the app in question was signed with the private key of a trusted party, like Apple does with its first-party apps.
Joshua Pitts, senior penetration testing engineer for security firm Okta, said he discovered the technique in February and informed Apple and the third-party developers about it soon after. Okta today also published information about the bypass, including a detailed disclosure timeline that began on February 22 with a report submitted to Apple and continues to today's public disclosure.
Ars Technica broke down how the method was used and which third-party tools are affected:
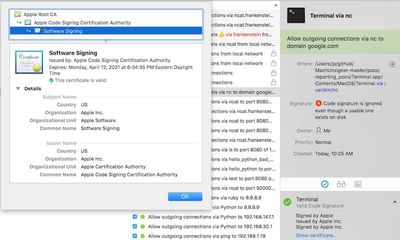
The technique worked using a binary format, alternatively known as a Fat or Universal file, that contained several files that were written for different CPUs used in Macs over the years, such as i386, x86_64, or PPC. Only the first so-called Mach-O file in the bundle had to be signed by Apple. At least eight third-party tools would show other non-signed executable code included in the same bundle as being signed by Apple, too.
Affected third-party tools included VirusTotal, Google Santa, Facebook OSQuery, the Little Snitch Firewall, Yelp, OSXCollector, Carbon Black’s db Response, and several tools from Objective-See. Many companies and individuals rely on some of the tools to help implement whitelisting processes that permit only approved applications to be installed on a computer, while forbidding all others.
Developer Patrick Wardle spoke on the topic, explaining that the bypass was due to ambiguous documentation and comments provided by Apple regarding the use of publicly available programming interfaces that make digital signature checks function: "To be clear, this is not a vulnerability or bug in Apple's code... basically just unclear/confusing documentation that led to people using their API incorrectly." It's also not an issue exclusive to Apple and macOS third-party security tools, as Wardle pointed out: "If a hacker wants to bypass your tool and targets it directly, they will win."
For its part, Apple was said to have stated on March 20 that it did not see the bypass as a security issue that needed to be directly addressed. On March 29, the company updated its documentation to be more clear on the matter, stating that "third-party developers will need to do additional work to verify that all of the identities in a universal binary are the same if they want to present a meaningful result."