Apple goes into great detail about the security of the Face ID facial recognition system built into the iPhone X in a security white paper and a support document, but relatively little has been said about the access that developers have to facial data captured by the TrueDepth camera, which has led privacy advocates and developers to express concerns about what apps can glean about you from your face.
A new piece from The Washington Post that includes commentary from both privacy experts and Apple itself explores the data third-party apps can access, echoing concerns previously brought up earlier this month.

Apps have no access to the facial map that Face ID uses to unlock your device, but developers are able to use the TrueDepth camera to scan a user's face for the purpose of creating more realistic augmented reality apps. As described by Apple:
Using the TrueDepth camera, your app can detect the position, topology, and expression of the user's face, all with high accuracy and in real time, making it easy to apply live selfie effects or use facial expressions to drive a 3D character.
Apps are able to see a full 3D face map along with a "live read-out" of 52 micro-movements in the eyelids, mouth, and other features. MeasureKit, a free app developed by Rinat Khanov, has a face mesh tool built in that displays the facial data the TrueDepth camera can capture along with a list of the facial expressions it tracks.
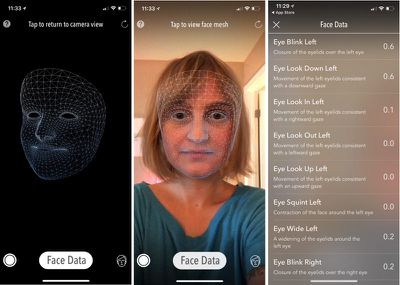
Apple has a privacy policy that's been in place since before the iPhone X launched requiring apps that use the TrueDepth camera to have a privacy policy, secure user consent option, and a clear outline of what data is being collected and how it's used, but The Washington Post's Geoffrey Fowler worries about the future implications of the TrueDepth camera, where such facial data could perhaps be used to determine gender, race, sexuality, or track facial expressions to determine medical conditions like depression.
"We take privacy and security very seriously," Apple spokesman Tom Neumayr said. "This commitment is reflected in the strong protections we have built around Face ID data--protecting it with the Secure Enclave in iPhone X--as well as many other technical safeguards we have built into iOS."
Khanov, the developer behind the aforementioned MeasureKit app, says Apple's policies may not be enough. Khanov didn't initially have a privacy policy in place in his app, and it was approved anyway. Apple said it was an oversight and asked Khanov to implement a privacy policy right away.
"There were no additional terms or contracts. The app review process is quite regular as well--or at least it appears to be, on our end," Khanov said. When I noticed his app didn't have a privacy policy, Khanov said Apple didn't require it because he wasn't taking face data off the phone.
As Fowler points out, apps that are using the TrueDepth camera are not currently providing enough information to customers. The popup to access the TrueDepth camera is the same generic popup that is required for the standard front and rear-facing cameras, and it does not mention that additional data is being collected.
Whether Apple will put stricter policies in place remains to be seen, as does how this kind of facial recognition data will be used in the future, but customers should be made aware of what's being provided to app developers. For those concerned, it's worth downloading the MeasureKit app or a similar app to see what's potentially being collected when an app accesses the camera on your iPhone X.























