Mozilla on Tuesday officially announced Firefox 57, the new "Quantum" version of its flagship desktop web browser for Mac, Linux, and Windows. Aside from a redesigned interface and a slew of new UI features, Mozilla says Quantum offers speeds twice as fast as Firefox 52 and a new engine that uses 30 percent less memory than Google Chrome.

The performance advantages are said to be down to Firefox's "just right" multi-process architecture, which uses separate processes to run its user interface and tabbed web page content. These additional processes are able to run across multiple CPU cores, making it much less likely for open web pages to negatively impact each other or the performance of the web browser in general.
While both Firefox and Chrome now run using multiple processes, Mozilla claims to have done things differently to avoid using up precious working memory. Chrome creates a separate content process for each open tab, and each tab typically consumes hundreds of megabytes of RAM, which has earned the browser a reputation as a resource hog.
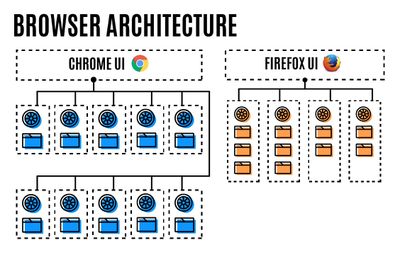
Where Quantum differs, claims Mozilla, is in its more conservative approach to using multiple processes. By default, Firefox now creates up to four separate processes for web page content, so the first four tabs each use those four processes, and additional tabs run using threads within those processes. This leads to multiple tabs within a process sharing the browser engine that already exists in memory, instead of each one creating their own.
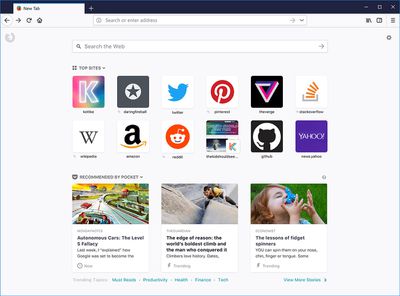
In addition to the under-the-hood improvements, the redesigned "Photon" user interface offers a less cluttered, more minimalist environment for browsing the web and aims to look better on modern high DPI displays. It also adds several new features including a built-in tool to take screenshots, and a new library for putting things like browsing history, bookmarks, Pocket lists, and synced tabs in one convenient place.
Firefox 57 also includes support for WebVR, which enables websites to take full advantage of VR headsets like the HTC Vive, while Mozilla's Pocket service is now more integrated in the browser and displays trending articles on the new tab page. Last but not least, a new feature called Tracking Protection blocks extensive requests for online user tracking. It works by default in the Private browsing window and Mozilla reckons it reduces the average page loading time by around 44 percent.
With all the changes, Firefox has had to lose support for many existing extensions written in XUL. Firefox Quantum only supports WebExtensions, which have more limitations, similar to Chrome extensions. Existing users can check the status of their extensions by navigating to Menu -> Add-Ons. Compatible ones are shown under "Extensions", while deactivated browser extensions appear under "Legacy Extensions" alongside an option to find the closest equivalent replacement available.
If you're already a Firefox user, you should receive an automatic upgrade to Quantum after restarting the browser. For everyone else, Firefox Quantum is available for macOS as a free download directly from the Mozilla website.


















Top Rated Comments
Is that what the fox said?
I'm done.