With a number of iPhone 8 and 8 Plus devices now in the hands of users, Ookla's network benchmarking suite Speedtest.net has been able to gather data on how the latest iPhones are performing compared to previous-generation models and has shared details with PCMag.
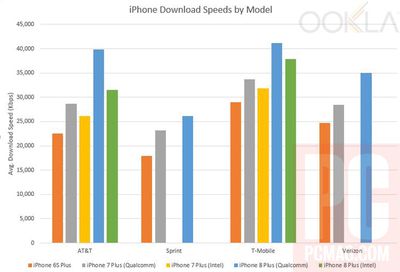
Based on data collected by Ookla, improvements appear to be around the 10 percent mark for most users, but users in Australia could expect up to nearly 25 percent faster speeds thanks to their network structure. Those users can expect up to the full 80 MHz carrier aggregation bandwidth in the phone due to Telestra's use of the appropriate bands.
Beyond speed comparisons to previous-generation iPhones, PCMag also compares the iPhone 8's cellular architecture to competing phones, such as the Galaxy S8.
The iPhone 8 is missing one of the components needed for gigabit LTE, or LTE category 16, in the US. The Qualcomm X16 modem can do Category 16, as we've seen on the Galaxy S8 and Moto Z2 Force. The phone supports 256QAM encoding and 4x carrier aggregation to 80MHz of spectrum, but not 4x4 MIMO antennas, which would improve both speed and signal strength. In theory, that would make this an 800Mbps phone, also known as LTE category 15.
The lack of 4x4 MIMO antennas is something we touched on at MacRumors on Tuesday. While the Qualcomm and Intel modems in the new iPhones are likely more power efficient, the cellular front-end and back-end supporting them are largely unchanged in structure from the iPhone 7 models.
The article goes on to point out can that this can result in loss of coverage due to deficient receiver diversity compared to other phones, complete with a New York subway test.
The lack of 4x4 MIMO is probably why the iPhone still falls short of the Galaxy S8 when it comes to recovering from dead zones, a notorious iPhone problem. We took an iPhone 8 and Galaxy S8 on the New York City subway, where they dropped in and out of T-Mobile coverage. The Galaxy S8 recovered faster in 8 out of 11 tests, and where it did, it was an average of 16 seconds faster than the iPhone at regaining LTE signal; when the iPhone won, it did so by 5 seconds on average.
Users looking for an unlocked iPhone should probably still opt for the Verizon or Sprint model, featuring the Qualcomm modem. While it boasts higher peak speeds than the Intel modems in aggregated user data, it is not clear whether it is superior for coverage, which would require more in-depth testing.
Finally, users looking ahead to the iPhone X should expect the same dichotomy of models and performance, given the iPhone X's tech specs page matches that of the iPhone 8 models in number of models and bands supported. The form factor will likely not have any impact on the antenna structures that will directly impact users in a meaningful way.
Moving forward, adopting 4x4 MIMO antenna structure would be one of the biggest advancements Apple could make for future iPhones' speed and coverage robustness.