The iPhone 8, 8 Plus, and X are equipped with a six-core A11 chip, which Apple says brings some major improvements over the A10 chip in the iPhone 7. The chip features two performance cores and four efficiency cores.
Early Geekbench scores for iPhone X and iPhone 8 devices suggest that not only does the new A11 significantly outperform the A10, it beats the A10X Fusion in the iPad Pro and it is on par with the chips in Apple's latest 13-inch MacBook Pro models.

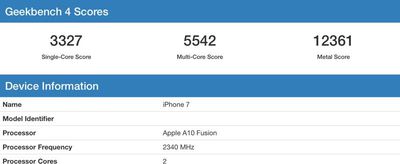
In 12 Geekbench scans, the A11 chip saw an average single-core score of 4169, and an average multi-core score of 9836. Some individual scores were much higher, though, with single-core scores topping out at 4274 and multi-core scores at 10438.
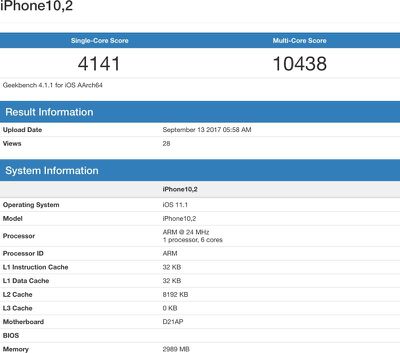
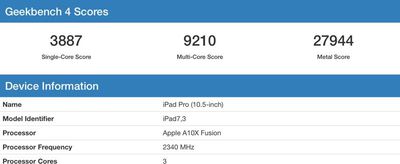
Comparatively, the 10.5-inch iPad Pro with A10 Fusion chip has an average Geekbench single-core score of 3887 and a multi-core score of 9210. Apple's highest-end dual-core 3.5GHz 13-inch 2017 MacBook Pro has a single-core score of 4592 and a multi-core score of 9602, suggesting the A11 outperforms it on multi-core tasks and comes close on single-core tasks.
Performance is even better stacked up against the lower-end 2017 MacBook Pro models. The 2.3GHz machine has scores of 4321/9183 and the 3.1GHz machine has scores of 4227/8955.
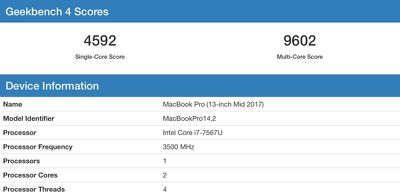
On paper, the iPhone X and iPhone 8 Plus will offer significantly better performance than the iPhone 7. The iPhone 7 has an average single-core Geekbench score of 3327 and a multi-core score of 5542.
According to Apple, the performance cores in the A11 chip are 25 percent faster than the A10 chip, while the efficiency cores are 70 percent faster than the A10 chip. The A11 chip is better at multi-threaded tasks because a second-generation performance controller is able to harness all six of the cores simultaneously.
MacRumors spoke to Geekbench's John Poole, who said he believes the A11 benchmarks are real. Poole believes the two high performance cores in the A11 are running at 2.5GHz, up from 2.34GHz in the A10. The 24MHz reading is an anomaly.
Though the iPhone X and the iPhone 8 offer impressive Geekbench scores, how that translates to real world performance remains to be seen. According to analyst Dan Matte, IPC (instructions per cycle) improvements are "relatively modest" and Geekbench scores should be ignored.
If you subtract out the efficiency gains from removing 32-bit support, you're left with maybe very roughly a 15% improvement in CPU IPC for the big cores, assuming equivalent clocks to the A10. Apple could have pushed performance and efficiency further, if not for 10FF being really bad. The era of the hyper Moore's Law curve in mobile is officially over, in my opinion, though maybe the A10 already signaled that. It's all rough sledding from here on out, based on the state of foundry challenges.
The iPhone 8, 8 Plus, and iPhone X all adopt the A11 chip, so with the iPhone 8 models set to launch next week, the improvements introduced in the A11 will become more clear.






















