In a new article by Wired today, Apple has shared the first in-depth look inside its new Apple Park campus, providing glimpses into the "Ring" building's original design, up-close images of the campus' construction and interiors, and even personal tidbits about former CEO Steve Jobs' connection to Apple Campus 2. As construction and updates on the site have stretched out over the years, current Apple CEO Tim Cook referred to Apple Park as the company's "biggest project ever."
Jobs' vision of the campus dates back to 2004, when he and Jony Ive began discussing a reimagined headquarters, but it wasn't until the company hired architect Norman Foster in 2009 that the plans began to ramp up. Meetings that Jobs had with architects working on the project lasted five or six hours, "consuming a significant amount of time in the last two years of Jobs’ life." Jobs was so deep into the project that he even knew at what time of year he wanted timber for the campus' walls to be cut.

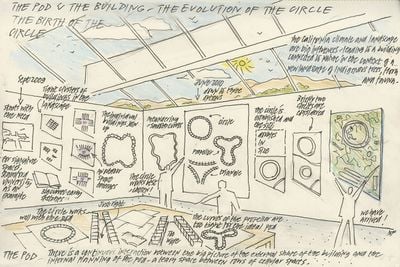
He also had an idea for creativity-boosting "pods," which would be specified for work, teamwork, socializing, etc, that eventually led to the original design of Apple Park to be represented as a clover leaf, or a propeller. Multiple factors eventually caused Jobs and the designers to push for a basic, circular shape, including the fact pointed out by Jobs' teenage son that the propeller looked like male genitalia from an aerial perspective.
As with any Apple product, its shape would be determined by its function. This would be a workplace where people were open to each other and open to nature, and the key to that would be modular sections, known as pods, for work or collaboration. Jobs’ idea was to repeat those pods over and over: pod for office work, pod for teamwork, pod for socializing, like a piano roll playing a Philip Glass composition. They would be distributed democratically.
Not even the CEO would get a suite or a similar incongruity. And while the company has long been notorious for internal secrecy, compartmentalizing its projects on a need-to-know basis, Jobs seemed to be proposing a more porous structure where ideas would be more freely shared across common spaces. Not totally open, of course—Ive’s design studio, for instance, would be shrouded by translucent glass—but more open than Infinite Loop.
By June 2010, Apple Park began a renewed life as the Spaceship building, or "Ring" as Apple calls it internally, that is now standing in Cupertino. Wired's article goes into the day in 2011 when Jobs, weeks before he passed away, pitched the campus to the Cupertino City Council. "I think we do have a shot," Jobs told the council, "of building the best office building in the world," after mentioning that if Cupertino failed to approve of the company's plans Apple could simply sell all of its property and move to somewhere nearby, like Mountain View.
Looking back at the fall of 2011, when he succeeded Jobs, Tim Cook remembered the last time he held a conversation with Jobs. Cook said he and Jobs were watching Remember the Titans and discussing the mundane aspects of Apple Park -- like figuring out which employees would reside in the main building -- that nevertheless "was something that gave [Jobs] energy."
Cook recalls the last time he discussed the campus with his boss and friend in the fall of 2011. “It was actually the last time I spoke to him, the Friday before he passed away,” Cook says. “We were watching a movie, Remember the Titans. I loved it, but I was so surprised he liked that movie. I remember talking to him about the site then. It was something that gave him energy. I was joking with him that we were all worried about some things being difficult, but we were missing the most important one, the biggest challenge of all.”
Which was?
“Deciding which employees are going to sit in the main building” and which would have to work in the outer buildings. “And he just got a big laugh out of it.”
The rest of the article goes into deep detail about the design and building materials Apple gathered when constructing Apple Park, and of course all the problems that came with construction. One roadblock was the canopies that are now adorned on the sides of the building, which Jobs was originally not a fan of, but were required to protect the all-glass building from the California sun.
Apple designers, including Ive's own design team, and Foster + Partners architects had to overcome problems like finding the perfect color tint to the canopies, and ensure they had the right curve to deflect rain.

The purpose of the giant glass sliding doors of the Ring's café -- for which Apple even patented a take-home pizza container -- was also inquired about by Wired:
“This might be a stupid question,” I say. “But why do you need a four-story glass door?”
Ive raises an eyebrow. “Well,” he says. “It depends how you define need, doesn’t it?”
Ultimately, the current designers and architects working on the campus believe that its end result represents Steve Jobs' vision exactly as he had it all those years ago. "I would say that the big picture has not changed at all," Foster mentioned. "If Steve could reappear, it would be as he conceived it when he last saw it as drawings. He’d find some of the details that were not addressed in his lifetime, but I believe he’d approve them."
The rest of Wired's look into Apple Park is worth a read, as it explores nearly every aspect of the campus' construction, from the staircases, ventilation, door handles, text fonts in the elevators, and more. According to Ive, "This is our home, and everything we make in the future is going to start here."