Last week, MacRumors covered photos of what appear to be the front and rear of bare iPhone 7 logic boards, and since that time we've been able to study these boards and compare them to previous iPhone generations' bare and populated logic boards.
Comparing the boards with existing component offerings and information suggests that Apple has indeed moved on from Qualcomm as its baseband modem supplier and switched to Intel for the upcoming iPhone generation. This does not preclude Apple from having other versions of the iPhone 7 or 7 Plus logic boards which feature a Qualcomm modem, such as an international model with differing LTE band options, as has been rumored.
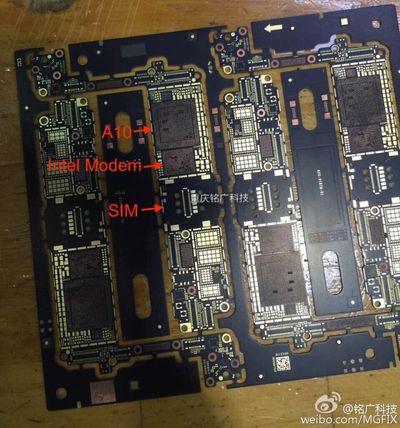

The image above shows the previously leaked and annotated logic board front with the probable location of the Intel baseband modem annotated. The pad pattern for the part in this location is markedly different than the pad pattern for the Qualcomm MDM9635, as shown in iFixit's parts catalog. The pad pattern of this mystery part also appears to match the dimensions listed on Intel's website for similar baseband modem offerings to the rumored XMM 7360 design solution.
Intel's SMARTi 5 RF transceiver, which accompanies the modem in Intel's reference solution, does not appear to be present on the iPhone 7 board, according to the package dimensions specific to the transceiver. It is always possible that the dimensions listed may be for a solution different than what Apple has used, whether it be custom or unannounced, but it appears as though Qualcomm could still be the supplier for the RF transceiver.
While there is not an exact pin match between the logic boards, the package size and overall number of pads on the reverse side is consistent with the WTR3925 and Qualcomm power management chips seen on the iPhone 6S and 6s Plus logic boards. The pad patterns also feature offset rows of pins, which have been historically exclusive to Qualcomm pad patterns on previous iPhones.
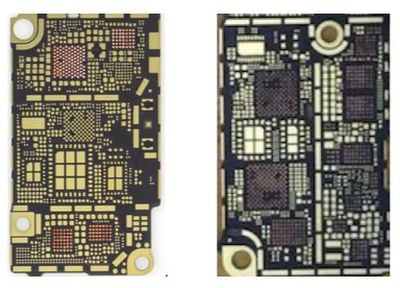
Near the space where the transceiver likely sits on the bottom rear, we've seen quite a few changes, as the separation metallization between RF chain and audio/battery components has gone from horizontal to vertical. As a result, the area dedicated to audio amplifiers and battery charger has grown. With the rumored removal of a headphone jack, it would seem that Apple is prime to remove one amplifier, although that is not evident from the leaked photo. With the display connection inversion and potential introduction of a capacitive home button, there are good reasons this area could have seen some growth.
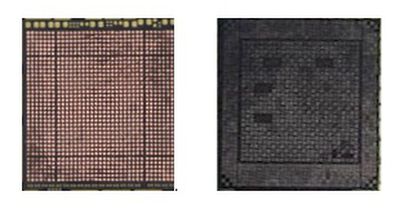
Finally, when looking at the A10, we notice a vacant row of pads near all four edges of the pad pattern. This is actually not new to the A10, as the A9 pad pattern also featured this. This is also somewhat common in large chips, such as desktop CPUs, where the inputs and outputs near the edge of the device have some separation from the device's core power and signals. What this resulted in for the A9 is package growth despite a small die shrink comparative to the A8.
Given that the A10 is likely to feature the same 16nm FinFET process as the A9, or some optimized variant thereof, it is very possible that we could see growth in die size without a huge jump in transistor count. As for TSMC's InFO packaging, it's still not clear whether this will drive package sizes at all for Apple's devices.
The A10's board footprint also features four rectangular boxes of missing pins. These may actually be spaces for small components directly under the package of the device. Generally, the performance of some chip components that are used for power filtering benefit most by being as physically close to the device pins as possible, and they are commonly placed directly on the backside of the PCB, connected by vertical metal interconnects through the board called vias, under chips with a large amount of digital switching functionality. For most mobile devices, that space is not available, but that could be one explanation for these sections of missing pins.
With a few weeks to go until the official iPhone 7 unveiling, it's possible we could still see leaks of the logic board populated with chips and other components, which would give us more information about component changes coming in the new device. Full details are unlikely to arrive, however, until teardown experts get their hands on the new iPhone and are able to dig into the components and even put them under a microscope.





















