According to a recent report from Taiwan's Commercial Times, via EE Times and a separate research report from KGI Securities' Ming-Chi Kuo, Taiwan-based TSMC may have won sole production rights on the A10 chip slated for the next-generation iPhone 7.
According to a recent report from Taiwan's Commercial Times, via EE Times and a separate research report from KGI Securities' Ming-Chi Kuo, Taiwan-based TSMC may have won sole production rights on the A10 chip slated for the next-generation iPhone 7.
This is in contrast to the split production of the A9 processor between Samsung and TSMC featured in the iPhone 6s and iPhone 6s Plus. Apple's decision to revert back to TSMC as a single supplier, as was seen in A8 chip production, could be motivated by advanced device packaging techniques offered by TSMC that may not have equivalents in Samsung's packaging offerings.
The Commercial Times report mentions TSMC's integrated fan-out wafer-level packaging (InFO WLP) technology as one of the key inclusions in the production contract. InFO WLP is one of many competing 3D IC technologies that promise higher levels of component integration in a single package with better electrical characteristics.
Among those improvements is the possibility for higher-width memory buses that support lower-power operation necessary for mobile devices, which for consumers means better performance and efficiency. 3D IC technologies are just beginning to emerge in the consumer space, with AMD's use of High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) in its Fiji XT line of discrete graphics cards being one of the first implementations.
According to a paper abstract from TSMC engineers, InFO WLP also allows for better thermal performance as well as superior performance for radio frequency (RF) components such as cellular modems. We reported last year about Apple hiring more engineers to potentially bring RF component development in house, so this packaging technology could serve as additional motivation to Apple for packaging in the future. Even if Samsung could offer Apple a comparable technology, the challenges of verifying a design on two new manufacturing flows may be a motivating factor for Apple to stick with one supplier for its next processor.
In the near term, the thermal advantages and potential increased memory bandwidth are the more immediate sources of improvement for Apple's potential next chip. Many 3D IC technologies have seen slow adoption due to increased costs and processing steps, but the simpler InFO WLP technology offers an easier, cheaper entry point for Apple, which also has the luxury of uncommonly high margins on its devices.
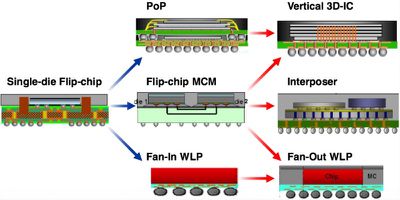
TSMC's InFO WLP differs from many competing 3D IC solutions in that it does not require an additional silicon interposer along with the existing package substrate used for component integration. Though they do not feature active components, silicon interposers are made on silicon wafers just like the application processors featured in mobile devices, making them a costly addition to the device assembly.
InFO WLP allows multiple flip chip components to be placed side-by-side on a package substrate resembling a traditional assembly, but with the ability to interconnect to one another through the package substrate. This is in contrast to traditional methods which feature stacked packages (package on package, or PoP) interconnected with tiny wires. As mobile memory technologies advance, with LPDDR4 being the latest iteration, electrical signaling becomes an increasing technological challenge which begins to make 3D IC technologies more attractive for enhanced performance.
The list of included components would not be limited to memory, however, so future device teardowns will be interesting as mobile devices begin to include these technologies. More information on TSMC's packaging technologies can be accessed via this PDF.