Apple's new iPad Air marks a significant technological step forward for the company, improving performance while reducing the device's volume and weight by over 25%. Much of the size and weight savings have been enabled by improved power efficiency, allowing Apple to reduce the device's battery thickness and capacity by roughly the same 25%.
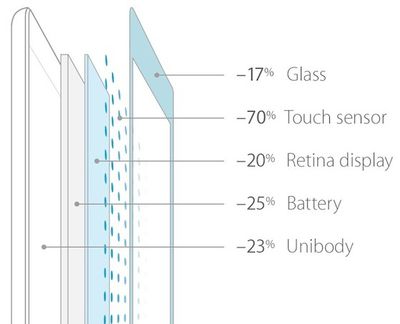
As noted in IHS iSuppli's component cost analysis released earlier today, the iPad Air now uses just 36 LEDs to light its display, down from as many as 84 in previous generations. Apple has also reduced the thickness of the display assembly, and so it appears that the display is indeed one of the areas where Apple has been able to make the most improvement on size and weight, both in the components themselves and in the battery capacity needed to drive them.
In a new analysis comparing the iPad Air's display to that of the Kindle Fire HDX 8.9 and the Google Nexus 10, Ray Soneira of DisplayMate Technologies confirms that Apple has indeed changed display technologies in the iPad Air, moving to indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO) semiconductor materials from the amorphous silicon (a-Si) compounds used in previous iPads. While rumors of Apple moving to IGZO for the iPad and other products have circulated for several years, Sharp has experienced difficulties ramping up production and it has taken until now for Apple to bring the technology to its products.
 Among the evidence cited by Soneira for his claim that the iPad Air has moved to IGZO technology are power measurements showing that the iPad Air's display offers a 57% improvement in power efficiency compared to previous iPads, a jump that simply would not be possible with a-Si technology. IGZO offers significantly better electron mobility than a-Si, allowing for much lower power requirements. The shift in technology has also enabled other improvements in the display of the iPad Air compared to its predecessor, and Soneira notes that Apple continues to offer an excellent display on its tablet lineup.
Among the evidence cited by Soneira for his claim that the iPad Air has moved to IGZO technology are power measurements showing that the iPad Air's display offers a 57% improvement in power efficiency compared to previous iPads, a jump that simply would not be possible with a-Si technology. IGZO offers significantly better electron mobility than a-Si, allowing for much lower power requirements. The shift in technology has also enabled other improvements in the display of the iPad Air compared to its predecessor, and Soneira notes that Apple continues to offer an excellent display on its tablet lineup.
Compared to the 4th generation, the screen Reflectance decreased by 23 percent, the Peak Brightness increased by 7 percent, and the Contrast Rating for High Ambient Light increased by 32 percent – all good. Absolute Color Accuracy and Image Contrast fidelity are very good (but somewhat below the Kindle Fire) and are discussed in detail below. The emphasis for the iPad Air is in reduced size, thickness, and weight. The most important under the hood display improvement is the switch from a-Si amorphous Silicon LCDs up to a much higher performance IGZO LCD backplane, which was discussed in our iPad 3 Display Shoot-Out article last year. The switch to IGZO produces an impressive 57 percent improvement in display power efficiency from previous Retina Display iPads – so the iPad Air doesn’t get uncomfortably warm like the earlier iPads.
MacRumors spoke with Soneira about the state of the display industry and Apple's potential plans for the future, and Soneira noted that he expects the Retina iPad mini launching later this month to also adopt IGZO technology. If anything, a move to IGZO is more important on the iPad mini than on the iPad Air due to higher pixel density on the smaller device, with a-Si being infeasible for a Retina display at that size.
While the iPad Air's display is excellent, Soneira notes Apple is no longer at the top of the heap, with Amazon's Kindle Fire HDX 8.9 display actually performing better than the iPad Air's display. This is made possible by Amazon's use of low temperature polysilicon (LTPS) technology, which offers even better performance and lower power requirements than IGZO.
LTPS is commonly used on displays for smaller devices such as the iPhone, but Amazon has pushed the technology to the edge by bringing it to tablet-sized displays despite high costs and complicated production. Apple is unlikely to follow Amazon's lead in the near future, in large part due to scalability issues that simply won't support the tens of millions of tablets Apple is producing each year.
IGZO also offers a more natural transition for display manufacturers, as they can in many cases simply upgrade their existing equipment from current a-Si production, while moving to LTPS would require a complete change in production. IGZO is also just the first of a number of metal oxide semiconductors that show promise for improved display performance, pointing to solid opportunities for the technology to continue to evolve.
Overall, Soneira notes that the iPad Air display has seen a very solid incremental upgrade, although he does have a few quibbles such as the continued presence of an air gap between the display and the cover glass when Apple has been moving toward laminating the two components together in other products. And with Amazon able to pursue LTPS technology for the Kindle Fire HDX due to its smaller size and lower unit volumes, Apple is finding itself facing stiffer competition in displays where it has long been the industry leader.