Apple Ranked as World's Top Semiconductor Customer in 2011
Back in June of last year, IHS iSuppli reported that Apple had become the world's largest buyer of semiconductors in 2010, jumping past HP and Samsung to top the list with $17.5 billion in spending. Apple's lead was expected to grow in 2011 on continued strength of the iPhone, iPad, and MacBook Air, all of which contain substantial NAND flash memory, which has become a primary driver of semiconductor markets due to the booming mobile device landscape.
Research firm Gartner is out today with a new report that appears to utilize a somewhat different methodology in calculating semiconductor expenditures but which now comes to the same conclusion as IHS Suppli's earlier report. According to Gartner, Apple became the world's largest semiconductor customer in 2011 as measured by total silicon content in all products designed by Apple and its competitors, known as Design TAM.
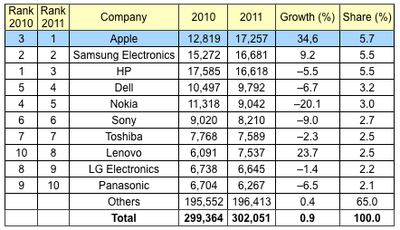
Gartner pegs Apple's year-over-year growth for 2011 at 34.6%, easily topping the growth of other top semiconductor customers and allowing it to leapfrog Samsung and a sliding HP for the top spot in the rankings. According to the report, semiconductor purchases for Apple's products came in at $17.3 billion in 2011, ahead of Samsung's $16.7 billion and HP's $16.6 billion purchases.
iSuppli's report from last year highlighted the vast differences in Apple's and HP's markets, with Apple's semiconductor usage being driven by mobile devices and HP's by traditional computer products. Gartner notes that mobile devices and solid-state drives are indeed now the major drivers of semiconductor usage.
"The major growth drivers in 2011 were smartphones, media tablets and solid-state drives (SSDs)," said Masatsune Yamaji, principal research analyst at Gartner. "Those companies that gained share in the smartphone market, such as Apple, Samsung Electronics and HTC, increased their semiconductor demand, while those who lost market share in this segment, such as Nokia and LG Electronics, decreased their semiconductor demand.
Gartner distinguishes Design TAM from Purchasing TAM, which would attribute to a given company only the amount actually purchased by the company. As an example of the difference between the two metrics, semiconductors purchased by a third-party manufacturing partner would generally count toward the primary company's Design TAM but not its Purchasing TAM.
Popular Stories
Apple released iOS 18.2 in the second week of December, bringing the second round of Apple Intelligence features to iPhone 15 Pro and iPhone 16 models. This update brings several major advancements to Apple's AI integration, including completely new image generation tools and a range of Visual Intelligence-based enhancements. Apple has added a handful of new non-AI related feature controls as...
Wednesday December 18, 2024 11:39 am PST by
Juli CloverApple is no longer planning to launch a hardware subscription service that would let customers "subscribe" to get a new iPhone each year, reports Bloomberg's Mark Gurman.
Gurman first shared rumors about Apple's work on a hardware subscription service back in 2022, and at the time, he said that Apple wanted to develop a simple system that would allow customers to pay a monthly fee to gain...
Blackmagic today announced that its URSA Cine Immersive camera is now available for pre-order, with deliveries set to start late in the first quarter of 2025. Blackmagic says that this is the world's first commercial camera system designed to capture 3D content for the Vision Pro.
The URSA Cine Immersive camera was first introduced in June, but it has not been available for purchase until...
Apple launched the controversial "trashcan" Mac Pro eleven years ago today, introducing one of its most criticized designs that persisted through a period of widespread discontentment with the Mac lineup.
The redesign took the Mac Pro in an entirely new direction, spearheaded by a polished aluminum cylindrical design that became unofficially dubbed the "trashcan" in the Mac community. All of ...
It's looking like 2025 is going to be an important year for Apple, with the company planning to revamp the iPhone, push further into smart home products, and improve Apple Intelligence. There are tons of new products rumored for 2025, including new iPhones, M4 Macs, a smart home command center, and much more.
We've highlighted the top five Apple products that will have the biggest impact in...
The current Apple TV 4K was released more than two years ago, so the streaming device is becoming due for a hardware upgrade soon. Fortunately, it was recently rumored that a new Apple TV will launch at some point next year.
Below, we recap rumors about the next-generation Apple TV.
Bloomberg's Mark Gurman last week reported that Apple has been working on its own combined Wi-Fi and...
Contrary to recent reports, the iPhone 17 Pro will not feature a horizontal camera layout, according to the leaker known as "Instant Digital."
In a new post on Weibo, the leaker said that a source has confirmed that while the appearance of the back of the iPhone 17 Pro has indeed changed, the layout of the three cameras is "still triangular," rather than the "horizontal bar spread on the...
Wednesday December 18, 2024 10:05 am PST by
Juli CloverElevation Lab today announced the launch of TimeCapsule, an innovative and simple solution for increasing the battery life of Apple's AirTag.
Priced at $20, TimeCapsule is an AirTag enclosure that houses two AA batteries that offer 14x more battery capacity than the CR2032 battery that the AirTag runs on. It works by attaching the AirTag's upper housing to the built-in custom contact in the...
![]()






















