A pair of reports today from Patently Apple reveal newly-published patent applications from Apple describing the company's work on advancing input systems for its Macs, showing off concepts for a multi-touch display embedded on the Magic Mouse and virtual keyboards with tactile feedback.
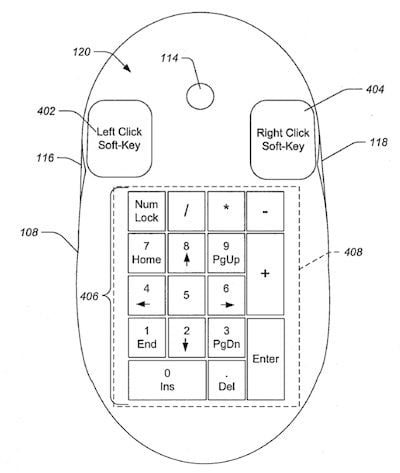
According to the first report, Apple's patent application entitled "Computer Input Device Including a Display Device" demonstrates how Apple could embed a multi-touch display on top of the company's existing multi-touch Magic Mouse, bringing new functionality to the input device.
Mighty Mouse with virtual number keypad
In one prominent example of the technology, Apple shows a virtual number keypad displayed on an Apple mouse very close in appearance to the company's Mighty Mouse that was shipping at the time of the patent application filing, allowing for easy data entry without the user needing to remove his or her hand from the mouse.
Apple discusses several options for how the display technology could be employed, but focuses primarily on using "collimated glass" fibers extending through the entire body of the mouse. Images to be displayed could be stored within the mouse itself, transmitted from a computer, or even simply be a magnified version of text or images located underneath the mouse.
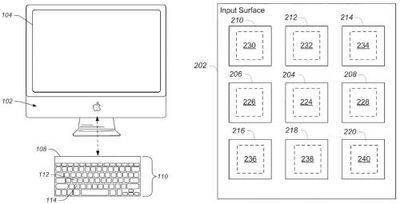
In its second report, Patently Apple points to an Apple patent application entitled "Method and Apparatus for Localization of Haptic Feedback", which describes the use of a virtual keyboard with mechanical actuators to allow the device to provide tactile feedback when keys are activated.
In particular, Apple discusses means of improving the localization of such haptic response to key activation, seeking to create a better user experience than that available through current haptic feedback input devices that typically vibrate the entire input surface upon key activation, a mechanism that is particularly troubling for multi-touch based systems. Apple's proposed system includes a significant number of actuators embedded under the display in locations where users are expected to engage key presses, combining those actuators with methods for suppressing the propagation of vibrations to keep them localized to the region of the key activation.
Such systems could lead to new virtual keyboards offering the flexibility of key layouts easily customized to the task at hand and yet retaining many of the benefits of current mechanical keyboards when it comes to tactile registration of keystrokes.