In a new article posted yesterday by Bloomberg, interesting details have been shared about one of Apple's secretive iPhone recycling plants. Detailing the "after-life of an iPhone," the piece focuses on the plant located in an industrial park in Hong Kong’s Yuen Long district and run by Apple contractor Li Tong Group, whose sole purpose is the deconstruction and recycling of iPhones, iPads, and Macs.
A few unnamed sources described Apple's recycling process as "the most rigid and exacting" when compared to other technology companies like HP and Microsoft. Apple typically exceeds the industry benchmark of collecting and recycling 70 percent of the devices produced seven years prior, according to Lisa Jackson, environmental affairs lead at Apple. It's known to reach marks as high as 85 percent.

"I think people expect it of us, I think our customers hold us to a high standard," Jackson said by phone from the company’s Cupertino headquarters. "It’s difficult, because these are incredibly complex pieces of product."
That standard would put the company currently allocating the equivalent of 9 million units of the iPhone 3GS from 2009. The yearly growth of the iPhone, subsequently resulting in more devices to churn in the future, has helped Li Tong Group grow as well, with the company expecting to open a new facility in San Francisco soon. The plant in Hong Kong currently holds about 300 employees.
The exact process of deconstructing the iPhone "is remarkably similar to Apple's production model, only in reverse," after users trade in or recycle an old iPhone at one of Apple's own retail stores or online. Unlike other companies who salvage certain components to aid in the repair of broken devices, Apple has "a full-destruction policy."
The recycling process is so specific to Apple that any iPhone scrap can't intermingle with another brand's devices, which is why the recyclers build dedicated facilities for the Cupertino-based company. Apple also regards the process as a step in increased safety, since it's getting potentially hazardous materials out of the hands of those in the public at risk during an unauthorized deconstruction.
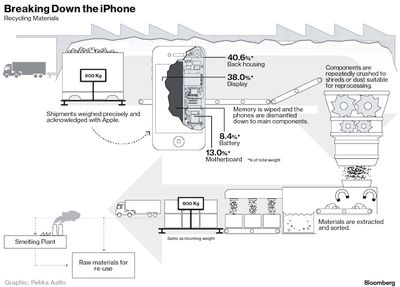
Apple pays for the service and owns every gram, from the used phone at the start to the pile of dust at the end, said Linda Li, chief strategy officer for Li Tong. The journey, consisting of about 10 steps, is controlled, measured and scripted through vacuum-sealed rooms that are designed to capture 100 percent of the chemicals and gasses released during the process, she said.
The process helps Apple avoid an abundance of counterfeit products flooding secondary markets. It's also another environmentally conscious feather in Apple's cap, siphoning the hazardous material within an iPhone into repurposed reincarnations like aluminum or glass tiles. "There's an e-waste problem in the world," Jackson said. "If we really want to leave the world better than we found it, we have to invest in ways to go further than what happens now."
Check out Bloomberg's full report on the Hong Kong recycling plant for more details on the process.























Top Rated Comments
We know consumers want the latest and greatest, and companies want to make them. This is a fantastic way to show responsibility for the waste that this cycle inevitably creates. And to that I say, well done.