Following our report yesterday about Apple expanding its trademark protection to use the "Apple" name in association with jewelry and watches in a number of countries, MacRumors has discovered that Apple may be quietly continuing to pursue trademarks on the "iWatch" name itself.
Evidence of Apple's interest in the iWatch name surfaced last June as the company began registering for trademarks on the "iWatch" name in a number of countries. Several major countries including the United States were not included in that list, and it was unclear whether Apple was holding off due to conflicts with pending trademark applications in those countries or if there were other issues in play.
At the time, reports mentioned several of those conflicting applications in the United States, but we now believe that one of those applications may in fact be Apple itself operating in disguise using a shell company by the name of Brightflash USA LLC. While MacRumors has yet to discover a smoking gun linking Apple to Brightflash, there are several pieces of circumstantial evidence pointing in that direction, thereby suggesting that Apple is indeed continuing to quietly lay the groundwork for an iWatch launch.
- Timing: Brightflash filed its iWatch trademark application in the United States on June 5, 2013, alongside the surge of applications by Apple in other countries during the span of June 3-5. While it is possible that the timing is a coincidence or the result of a separate company moving extremely quickly to apply for the mark after news of Apple's applications in other countries started breaking on June 5, this would appear to be unlikely.
- Concealed company structure and location: Brightflash is registered in Delaware, a common location for incorporation due to the state's business-friendly laws. According to state records, Brightflash was formed on June 27, 2012 and the company uses the Corporation Trust Center in Wilmington, Delaware as its address. That building serves as the home of hundreds of thousands of companies, streamlining the process of locating in Delaware and providing a level of anonymity for companies registering using the firm's services.
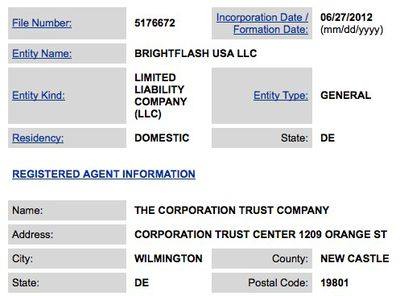
- Few leads on company representatives: Efforts to determine Brightflash's executives and representatives have proven difficult as well, with the initial trademark application using attorney John Sullivan at the same Corporation Trust Center address. Last month, Brightflash filed a change of attorney form with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office listing a David Harris also at that address, with that document signed by a manager "J. Yori". It is possible that this is Joan Yori, an executive with Stewart Management Company, a firm offering services for establishing so-called special purpose entities.
SMC offers a full service domicile management package including office space, employees, officers and directors, accounting services, and coordinates services with recommended local legal and banking providers.
- Legal links from Ecuador: As we noted yesterday, Apple filed for a trademark on the "Apple" name in Class 14 (jewelry and watches) in Ecuador last December, and the attorney who facilitated that application was Alejandro Ponce Martinez, a principal attorney with Quevedo & Ponce in Quito. Ponce has helped Apple with a number of other trademark applications, including recent filings for iOS 7 icons and iPad Air, and just weeks prior to the Apple jewelry filing he helped Brightflash file its application (PDF: page 164) for the "iWatch" mark.
In an initial response to Brightflash's U.S. application for the iWatch trademark, the examiner cited several prior pending applications from other firms that would potentially be confusing with Brightflash's desired usage. As a result, Brightflash late last month filed its own response requesting that its application be put on hold until the other pending applications were either granted or abandoned. Last week, the patent examiner issued a letter granting the suspension of Brightflash's application for the time being. If Brightflash is indeed Apple, the company would very likely make an effort to acquire the rights to any of the other trademarks if they are granted.
Brightflash continues to file trademark applications in other countries, including Australia and Macau. And just last month, United Kingdom and Denmark were added to the list, indicating that the firm is indeed still interested in protecting the iWatch name. As noted by French site Consomac [Google Translate], Brightflash is pursuing registration of the iWatch name in at least four dozen countries around the world.
Brightflash is also attempting to trademark the "Brightflash" name itself in a number of countries, and it is unclear whether this is simply part of the process of pursuing the iWatch mark or if there is an additional feature or product that could use the Brightflash name.
In the background of any efforts by Brightflash or Apple to secure a U.S. trademark on the iWatch name is a years-long battle between Swiss watchmaker Swatch and New York firm M.Z. Berger. MZB applied for a U.S. trademark on the iWatch name back in July 2007 and the application was nearly approved before Swatch opposed the mark on two fronts: potential confusion with the Swatch brand and a lack of intent by MZB to actually use the iWatch name.
An appeals board has ruled that MZB should not be awarded the trademark on the basis that there is no evidence of MZB's intent to use the iWatch name at the time of filing, although Swatch's claim of potential confusion was not found to be warranted. Both parties appealed the respective decisions against them late last year, and the case remains unresolved.
Apple's potential use of Brightflash as a shell company to hide its efforts to protect intellectual property would certainly not be the first time the company has engaged in such tactics. Last November, the company created an entity by the name of CarPlay Enterprises to file a U.S. trademark application on the term "CarPlay", which last month became the new name for the previously named iOS in the Car feature in iOS 7.1.
In an earlier example leading up to the launch of the iPad, Apple used a shell company by the name of Slate Computing to protect "iSlate" and "MagicSlate" while using a separate firm under the name IP Application Development to secure the "iPad" name.

















