The New York City Council is considering a new measure to help fight iPhone and other smartphone thefts, in the form of a pawn shop bill that would require second hand dealers and pawn brokers to maintain easily accessible electronic records of purchased items, including photographs and serial numbers. Current law mandates non-electronic inventory records.
According to the New York Daily News, police believe such a measure would make it easier to search for stolen smartphones, Apple products, and other items, though pawn shop owners have opposed the bill, declaring it an invasion of customer privacy.
iPhone and iPad thefts continue to be a major issue for law enforcement, despite ongoing efforts to implement various theft deterrent programs. As noted earlier this year, in 2012 there were 16,000 "Apple picking" thefts in New York city, which accounted for 14 percent of all crime. As of last week, 45 percent of robberies involved cell phones, and half of those stolen devices were iPhones.
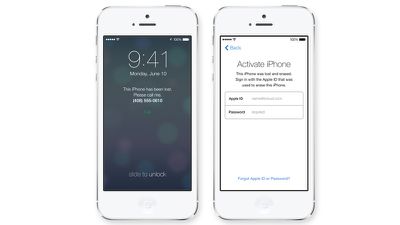
While Apple introduced Activation Lock with iOS 7, preventing stolen phones from being reactivated without an iCloud password, theft of Apple products continues to be an issue for users who have not activated iCloud or upgraded to iOS 7.
Both San Francisco district attorney George Gascón and New York Attorney General Eric Schneiderman, who have spearheaded anti-theft efforts, have praised Activation Lock, calling it the "world's first attempt to implement a technological solution to the global smartphone theft epidemic."
The two have also been pushing other cellphone makers to implement kill switches, allowing for the remote deactivation of a stolen phone. Yesterday, The New York Times reported Gascón had been working with Samsung on such an antitheft feature, but was running into trouble getting wireless carriers to cooperate.
While Apple has struck a deal with carriers that disallows them from controlling the software on iOS devices, other carriers, which ship with the Android operating system, do not have similar deals. Carriers are able to install proprietary software and have some measure of control over what manufacturers install on the phones as well.
Mr. Gascón said that, based on e-mails he had reviewed between a Samsung executive and a software developer, it appeared that the carriers were unwilling to allow Samsung to load the antitheft software. The emails, he said, suggest that the carriers are concerned that the software would eat into the profit they make from the insurance programs many consumers buy to cover lost or stolen phones.
According to the CTIA, an industry trade group that represents carriers, kill switches are not an acceptable anti-theft solution, as it introduces a method for hackers to remotely disable phones. The CTIA and the four major wireless carriers in the United States have instead backed a centralized database designed to track stolen phones, but it has reportedly been largely ineffectual.
Gascón has said that he is evaluating what actions to take against the carriers for refusing to allow Samsung to implement a kill switch on its phones, and has said that he will force them to "prioritize the safety of their customers over additional money in their pockets."
As for the pawn shop bill, it remains under consideration. New York City lawmakers have also recently introduced legislation that would make it illegal for businesses to sell used smartphones without obtaining proof of ownership.